Top 7 People Counting Solutions
(and why Computer Vision wins)
The rapid rise of Computer-Vision-based people counting solutions has a familiar feel to it…
As recently as the early 20th century, everybody knew that stagecoaches were the most reliable way to travel. Afterall, horse and cart had been transport’s mode of choice since Roman times. So naturally, when the first ‘horseless carriages’ appeared on the scene, many considered them a fleeting fancy. Henry Ford saw it differently.

As history.com notes: “The Model T, sold by the Ford Motor Company from 1908 to 1927, was the earliest effort to make a car that most people could actually buy”. This approach, and it’s relative accessibility compared to the first motorvehicles, radically and perminanetly transformed everyday travel.
Like the automobile of the early 1900s, computer vision software is on the cusp of fundamentally changing how we produce data and generate analytical insights about the physical world.
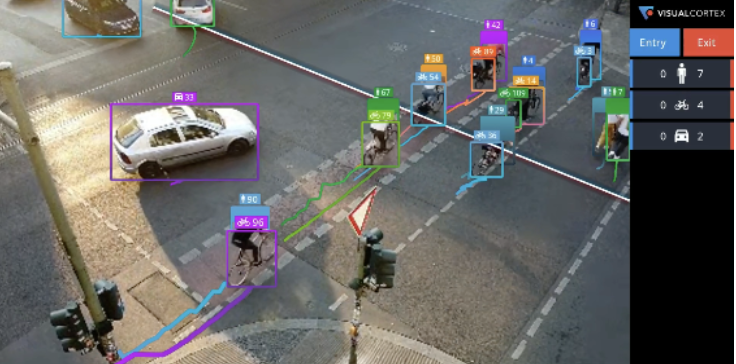
With a new focus on scalability, usability, video metadata creation and scalabiltiy, video analytics technology is now poised to disrupt the people counting sector in the same way that Ford’s Model T reshaped transportation.
Most popular people counting solutions and their drawbacks
To uderstand why existing human-reliant, hardware-based and server-side people counting technology fall short, we’ve compiled a summary of the most popular computer vision alternatives, including their benefits and shortcomings:
Manual Counting
Pros: Minimal technical skills or tools required.
Cons: Ludicrously labor-intensive and time-consuming; prone to human-based errors, including fatigue, distraction, and counting bias. Inability to provide real-time data; no metadata logging to facilitate advanced analytics; and linear scalability are further drawbacks.

Infrared Beam Counting
Pros: Low power consumption; privacy-friendly; relatively inexpensive.
Cons: Temperature changes, drafts and ambient light affect accuracy; while limited field-of-view make counting in large or open spaces hard. Intelligence gathering is constrained to basic counts; fixed-position sensors are prone to occlusion issues; and the only way to scale is to purchase more equipment.
Laser Beam Counting
Pros: Useful for outdoor counting
Cons: Can only cover a narrow path; may pose safety threats if not installed and maintained properly; while reliance on physical equipment makes scalability hard. Laser counting is also prone to multiple factors impacting accuracy, including obstructions, reflections, lighting conditions and fast movements.

Thermal Imaging Counting
Pros: Comparatively effective in low light conditions.
Cons: Narrow field-of-view confines usage to smaller enclosed spaces; intelligence gathering is constrained to basic counts; and is more expensive than other technologies. Poor comparative accuracy is a major consideration, with crowded areas, clothing types, weather conditions and ambient temperature all impacting its ability to effectively detect people via body heat.

Wifi Counting
Pros: Able to count people without additional hardware or sensors; can also capture additional data, including dwell-time and movement patterns.
Cons: Limited coverage (inappropriate for large spaces and is easily disrupted by common physical obstacles, such as walls and furniture) and questionable accuracy (susceptible to interference, attenuation and reflections, with signals also disrupted by other Wifi-enabled devices using the network). Wifi counting can also inadvertently reveal sensitive information about individuals, including device data.
Bluetooth Counting
Pros: Can provide some additional data, including dwell-time and movement patterns.
Cons: Limited signal range; requires a high level of technical expertise to implement and maintain; and additional hardware or sensors may be required to collate and process data. Accuracy is affected by interference, attenuation, reflections and other devices in the count area. It can also inadvertently reveal sensitive information about individuals, including device data.
Why Computer-Vision-based people counting solutions come out on top
Modern video analytics software addresses many of the inherent pitfalls historical appraoches to people counting:
1. Metadata is produced and logged about detected objects and actions, making advanced anlaytics – beyond basic counts – possible
2. Whether batched or live, data is processed far more efficiently
3. Real-time detections and streaming analytics are attainable
4. Results are more reliable: Machine Learning models for people counting are less prone to environmental and network disruptions, obstructions and occlusion, which impact accuracy
5. Digital deployment means that Computer-Vision-based people counting solutions can be applied to many more scenarios and scaled broadly – without the coverage limitaitons, install expenses and maintenance logistics of hardware-dependent tech
For details, and to discover the how behind the why, check out our white paper, People Counting and Pedestrian Analysis with Computer Vision.




